

---The article comes from the Internet---
Special engineering plastics, also known as high-performance polymers, are generally developed according to the needs of special applications. Compared with general engineering plastics, the performance is superior and unique, and the long-term use temperature is above 200 °C.
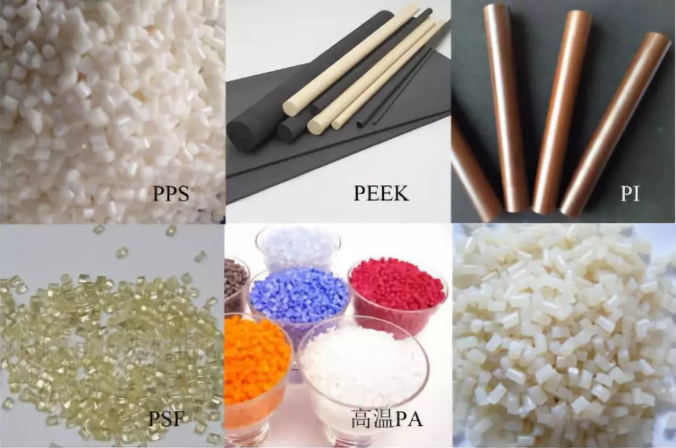

Since the advent of polyimine (PI) in the 1960s, the main varieties developed and industrialized are polyimine (PI), polyamine imine (PAI), polyetherimide (PEI), polyphenylene sulfide. (PPS), polysulfone (PSF), polyethersulfone (PES), polyetheretherketone (PEEK), liquid crystal polymer (LCP), and fluoroplastic. Today we briefly introduce 7 kinds of special engineering plastics.
Polyetheretherketone is a linear aromatic semi-crystalline thermoplastic. It is a legendary special engineering plastic with exceptionally high performance special engineering plastics. It has been an important strategy since its inception. Defense military materials.
Full name: Polyetheretherketone
Synthetic method: polycondensation
Melting point: 334 ° C
Glass transition temperature: 143 ° C, its glass fiber or fiber reinforced grade can be used at 250 ° C for a long time.
Advantages: low creep, high modulus of elasticity, excellent friction properties, especially resistance to friction, resistance to various media and excellent chemical resistance.
Disadvantages: insoluble in industrial solvents, difficult to synthesize, relatively low yield, low glass transition temperature, etc.
Applications: Electrical and electronic, mechanical, automotive, petroleum exploration, medical, protective coatings, etc.

Figure PEEK screw
Spine internal fixator
Polyphenylene sulfide, also known as polyphenylene sulfide, polyphenylene sulfide, was born in 1973, although the development time is only 40 years, but the potential is great, known as the sixth largest engineering plastic, is Chinas independent industrialization Special engineering plastics.
Full name: polyphenyl sulfide
Synthesis method: Ma callum method, condensation method, Philips method
Melting point: 280~290°C
Decomposition temperature: 430~460°C (in air)
Crystallinity: up to 65%
Advantages: Excellent thermal stability, long-term use temperature is the highest in thermoplastic materials, up to 220~240 °C, excellent creep resistance.
Disadvantages: The profile has weak impact resistance and very low elongation at break.
Application areas: electrical and electronic, machinery, automotive, flame retardant accessories, etc.
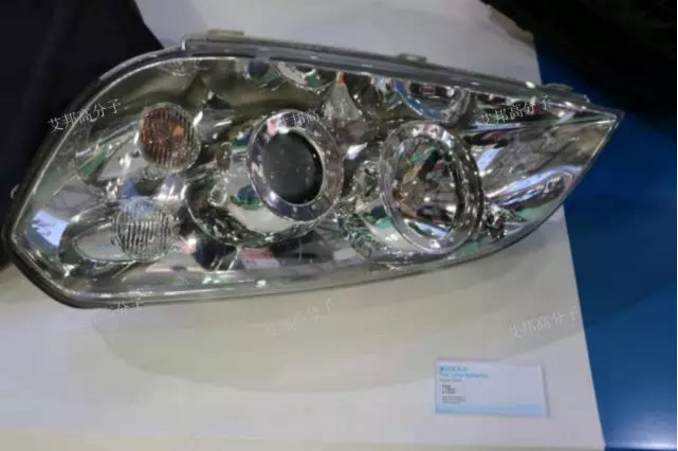

Figure Solvay fog light reflector
Polysulfone PSF
There are three kinds of common bisphenol A type PSF, polyether sulfone and polyaryl sulfone.
Full name: polysulfone
Heat resistance: polyarylsulfone>polyethersulfone>polysulfone
Processability: Polyarylsulfone = Polysulfone > Polyethersulfone
Advantages: excellent mechanical properties, high strength, high modulus, high hardness, low creep, heat resistance, cold resistance, aging resistance, high heat distortion temperature, good chemical stability, resistance to inorganic acid, alkali, salt liquid erosion It has excellent electrical insulation, radiation resistance and self-extinguishing properties.
Disadvantages: Not resistant to polar organic solvents, such as ketones, esters, chloroform and other fatigue resistance.

Figure Polyethersulfone pipe valve
In 1972, GE Company of the United States began research and development of PEI. After 10 years of trial production and trial use, it built a 5,000-ton production unit in 1982 and officially sold it in the market with the product Ultem.
Full name: polyetherimide
Melting temperature:340~415 °C, can be used for a long time at -160~180 °C working temperature.
Glass transition temperature: 215 ° C
Drying temperature: 150 ° C
Advantages: high temperature resistance, high strength, high modulus and a wide range of chemical resistance, flame resistance, low smoke emission, high dielectric constant and loss factor.
Defect: The linear expansion coefficient is high, and the pure resin is prone to brittle fragmentation at the initial stage of friction.

Figure Temperature-resistant polyetherimide (PEI) film
Polyimide PI is a kind of aromatic polymer with an imide ring in the macromolecular backbone. It is divided into thermosetting PI and thermoplastic PI. It is a typical organic polymer material. Thermoplastic PI molding temperature is high, and small molecules play a role in the release of the hair, so the application of composite materials is not extensive. Thermosetting PI is different. It uses a low molecular weight, low viscosity monomer with a crosslinkable end group and its prepolymer as a starting material, and curing is completed by heating, which fundamentally improves the processability.
Full name: Polyimide
Synthetic method: polycondensation
Decomposition temperature: about 500 °C
Advantages: high temperature and low temperature, chemical resistance, good dimensional stability, self-extinguishing, low toxicity, good biocompatibility, etc.
Disadvantages: difficult processing, poor water resistance, high price
Application areas: aviation, defense, microelectronics, nano lasers, etc.
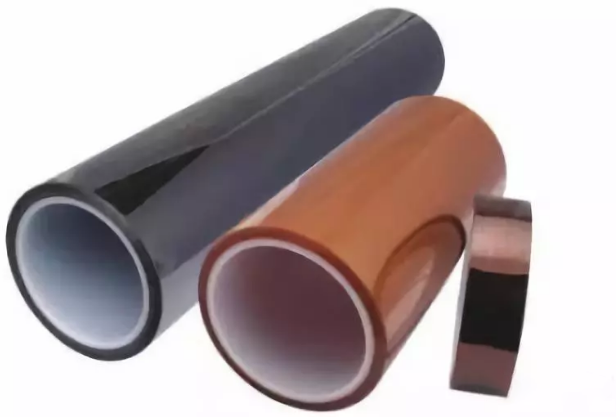

Polyimide film
As the first of the five engineering plastics, nylon was born earlier. It has a wide range of applications, and its output is very large. There are many kinds of nylon. The traditional nylon is generally used at temperatures not exceeding 200 ° C, which is a major disadvantage of nylon itself. National scientists have developed high temperature resistant nylon materials as needed.
Classification: PA46, PA6T, PA4T, PA12, PA10T, PA9T, etc.
Synthesis method: copolymerization, condensation
Advantages: low temperature and high temperature resistance, chemical resistance, excellent mechanical properties, electrical insulation and electrical stability, easy to process.
Disadvantages: need to add fillers to have water, flame retardant, high temperature and other properties.
Application areas: automotive bearings, engine parts, etc.
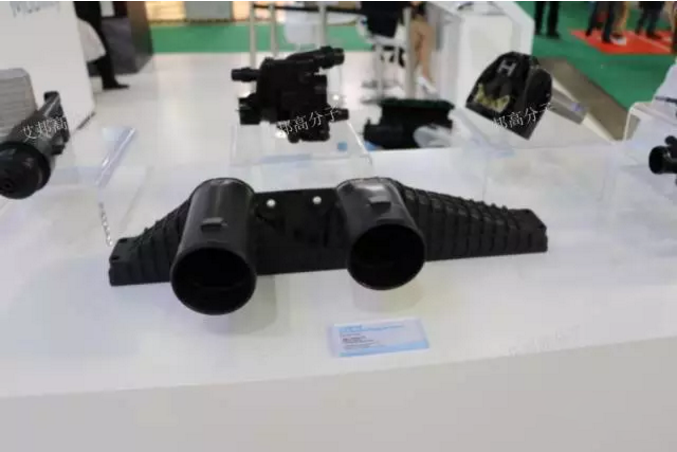

Figure Solvay intercooler air chamber
Full name: liquid crystal polymer
No fixed molecular structure, can combine monomer polycondensation according to performance requirements
Injection temperature: 301 ~ 350 degrees Celsius
Drying temperature: generally 160~180°C
Advantages: self-increasing, excellent thermal stability, heat resistance and chemical resistance, excellent flame retardancy, outstanding corrosion resistance.
Disadvantages: Trace moisture must be dried before being adapted, and the moisture content can be reduced to 0.03% before use.
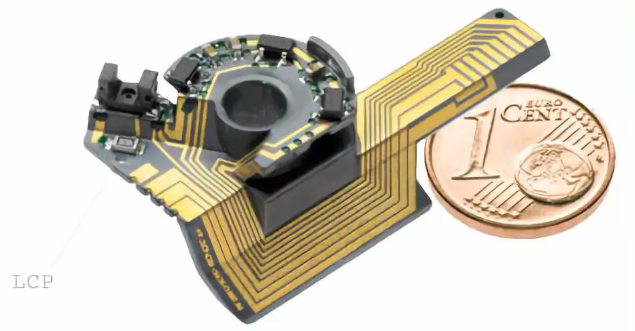
Figure LCP precision instrument

Figure Blonde LCP
Address: Building 2, No.66 Feidu Rd, Nanhui New Town, Pudong New District, Shanghai, China
Phone: 021-68256865
Fax: 021-68256255

© 2009-2022 ZhongLei New Material Science Co.,Ltd Copyright Shanghai ICP 18046883Number-1